|
One of the early breakthroughs for nanotechnology was its success in visualising individual atoms and molecules. Nowadays, we can not only visualise molecules, but also capture videos of how they move. Yet at the nanoscale, how do you know if such motion is related to molecular dynamics, and not simply due to measurement noise? In a study published in the journal ACS Nano, we have developed methods to answer this question.
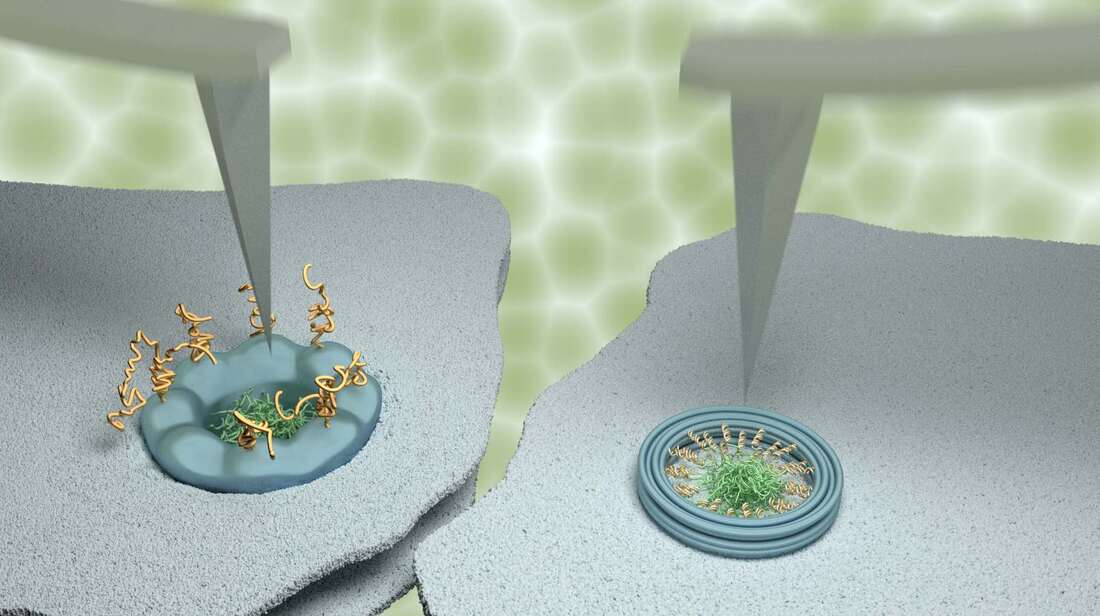
Our study made extensive use of a technique named atomic force microscopy. This type of microscopy uses an ultrafine needle to feel rather than see molecules on a surface, similar to a blind person reading Braille. The needle repeatedly scans the surface to produce an image that refreshes fast enough to track how molecules or groups of molecules change with time. To demonstrate the power of our methods, we focussed on tiny channels in the protective membrane that surrounds the nucleus in our cells. For the appropriate use of genetic material in the nucleus, these ‘nanopores’ selectively allow the entrance and exit of certain molecules, while blocking others to protect genetic material and normal functions of the cell. The results were compared with data obtained on artificial nanopores – built by collaborators at Yale University – that replicate several properties of the natural nanopores in the nuclei of our own cells. Whereas the artificial nanopores showed unambiguous signatures of molecular motion, this was much less clear for the natural pores. In agreement with results previously reported by some other labs, some (sub)nanometre fluctuations were detected; yet upon closer inspection, these fluctuations turned out to be indistinguishable from fluctuations measured away from the nanopores, and were therefore attributed to measurement noise. We explain the difference between the natural and artificial nanopores by the presence of other proteins that are involved in the transport and that in the natural nanopores act as a glue preventing or restricting the motion of other molecules. This work was kindly supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). Joint first authors and PhD students George Stanley and Bernice Akpinar are part of, respectively, the BBSRC London Interdisciplinary Doctoral Programme (LIDo) and the joint UCL/Imperial College London Centre for Doctoral Training in the Advanced Characterisation of Materials. |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed